Office 365 is one of the most popular and widely-used cloud-based productivity suites in the world. It offers a range of applications and services that help users to create, collaborate, and communicate online. However, as with any cloud-based platform, Office 365 also comes with some security risks and challenges that users need to be aware of and address.
Office 365 is one of the most popular and widely-used cloud-based productivity suites in the world. It offers a range of applications and services that help users to create, collaborate, and communicate online. However, as with any cloud-based platform, Office 365 also comes with some security risks and challenges that users need to be aware of and address.
What are the main security risks of Office 365?
Some of the common security concerns that Office 365 users face are:
- Sensitive data leakage: Office 365 stores and processes a lot of sensitive and confidential data, such as personal information, financial records, intellectual property, and trade secrets. If this data is not properly protected and controlled, it can be leaked or exposed to unauthorized parties, resulting in reputational damage, legal liability, or competitive disadvantage.
- Privilege abuse: Office 365 users have different levels of access and permissions to various resources and functions within the platform. If these privileges are not managed and monitored properly, they can be abused or misused by malicious insiders or compromised accounts, leading to data theft, sabotage, or fraud.
- Credential theft: Office 365 accounts are often targeted by cybercriminals who use various techniques, such as phishing, malware, or brute-force attacks, to steal user credentials and gain access to their data and services. Once inside, they can impersonate users, send malicious emails, download files, or perform other malicious actions.
- Unauthorized or external file sharing: Office 365 enables users to easily share files and folders with other users within or outside the organization. However, if this feature is not configured and governed properly, it can lead to unauthorized or accidental sharing of sensitive data with unintended recipients or third parties.
How to protect yourself from Office 365 security risks?
To mitigate the security risks of Office 365 and enhance its security posture, users can follow some best practices, such as:
- Use Microsoft Information Protection (MIP): MIP is a unified set of capabilities that help users to discover, classify, label, protect, and monitor their sensitive data across Office 365 applications and services. Users can apply sensitivity labels to their documents and emails that indicate the level of confidentiality and associate them with protection policies and actions, such as encryption, visual marking, access control, or data loss prevention. Users can also apply sensitivity labels to Microsoft Teams sites, SharePoint sites, or Microsoft 365 groups to ensure appropriate device and privacy settings.
- Use a third-party backup and recovery solution: While Office 365 provides some native backup and recovery capabilities, they are often limited in scope and duration. For example, deleted items are only retained for a maximum of 93 days in the Recycle Bin. To ensure that their Office 365 data is properly backed up and can be restored in case of accidental deletion, corruption, ransomware attack, or legal dispute, users should use a third-party backup and recovery solution that offers granular, flexible, and reliable backup and restore options.
- Use an email security solution with anti-phishing capabilities: Phishing is one of the most common and effective ways to compromise Office 365 accounts. To prevent phishing attacks from reaching their inbox or tricking them into clicking on malicious links or attachments, users should use an email security solution that can detect and block phishing emails based on various indicators, such as sender reputation, domain spoofing, content analysis, or behavioral analysis. Users should also be educated on how to spot and report phishing emails.
- Use multi-factor authentication (MFA): MFA is a security feature that requires users to provide more than one piece of evidence to verify their identity when signing in to their Office 365 account. This can be something they know (such as a password), something they have (such as a phone), or something they are (such as a fingerprint). By enabling MFA for their Office 365 account, users can add an extra layer of protection against credential theft and unauthorized access.
Conclusion
Office 365 is a powerful and convenient cloud-based productivity suite that offers many benefits for users. However, it also comes with some security risks that need to be addressed and managed. By following the best practices mentioned above, users can improve their security hygiene and enjoy Office 365 without compromising their data privacy and security.
Videos
Pro Tech Show: 7 Things to Know Before Using Office 365
Risk Management with Microsoft 365 | Advisicon
Other factors:
No Impact on SLA?
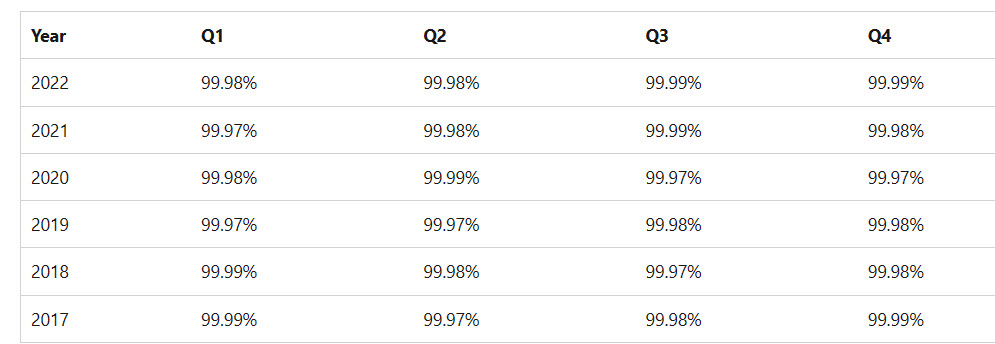
Microsoft offers a financially-backed service level agreement for its cloud services, with compensation available to customers if the service achieves less than its 99.9% commitment. Its website lists recent SLA worldwide performance for Microsoft 365 (Figure 2).
Here’s a table representing the downtime in hours for availability levels ranging from 99.99% to 99.9%:
| Availability (%) | Downtime per Year (hours) |
|---|---|
| 99.99% | 0.876 hours |
| 99.98% | 1.752 hours |
| 99.97% | 2.628 hours |
| 99.96% | 3.504 hours |
| 99.95% | 4.380 hours |
| 99.94% | 5.256 hours |
| 99.93% | 6.132 hours |
| 99.92% | 7.008 hours |
| 99.91% | 7.884 hours |
| 99.90% | 8.760 hours |
These values represent the annual downtime for each corresponding availability percentage.